Ecosystems are showing symptoms of resilience loss
Swedish Young Academy of Sciences
Forest to savanna
Regime shifts are large, abrupt and persistence critical transitions in the function and structure of (eco)systems
Coral transitions
Regime shifts are large, abrupt and persistence critical transitions in the function and structure of (eco)systems
Fisheries collapse
Regime shifts are large, abrupt and persistence critical transitions in the function and structure of (eco)systems
Where are regime shifts likely to occur?
Depends on our ability to observe and measure resilience
Data & methods
- Terrestrial:
- Gross primary productivity (2001:2018) - Ecosystem respiration (2001:2018) - Leaf area index (1994:2017) - Marine:
- Chlorophyll A (1998:2018) - >1M pixels, weekly obs, 0.25 degree grid resolution
- ↑ Variance and autocorrelation
- Δ skewness and kurtosis
Dakos et al. 2012. PLoS ONE; Kéfi et al. 2014. PLoS ONE
Critical speeding up
- ↓ Variance and autocorrelation
Titus & Watson 2020 J Theor Ecol
Fractal dimension
- ↑ adaptive capacity
- Measure of self-similarity across scales
West, Geoffrey. 2017. Scale; Gneiting et al. 2012. Statistical Science.
Analysis: one pixel
![]()
The generic resilience indicators do not necessarily align with critical slowing down or speeding up theories
Rocha, JC. 2022. Ecosystems are showing symptoms of resilience loss. ERL
Detection
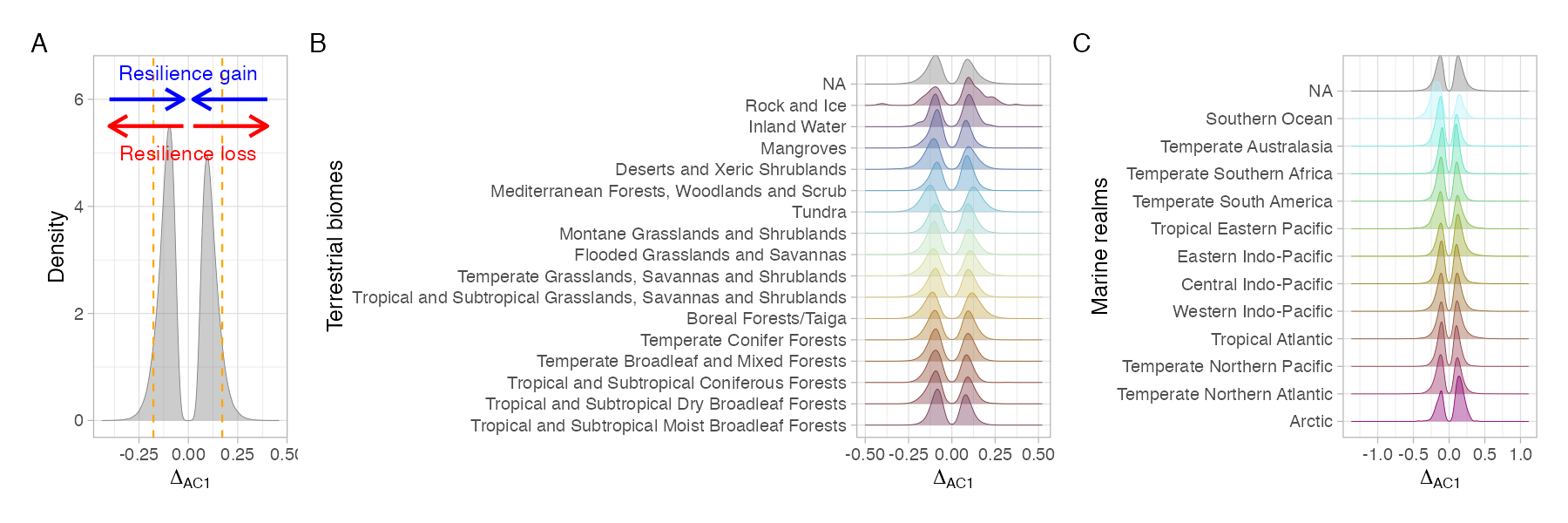
In the absence of ground truth, if Δ is > 95% or < 5% of the distribution is considered a signal of resilience loss
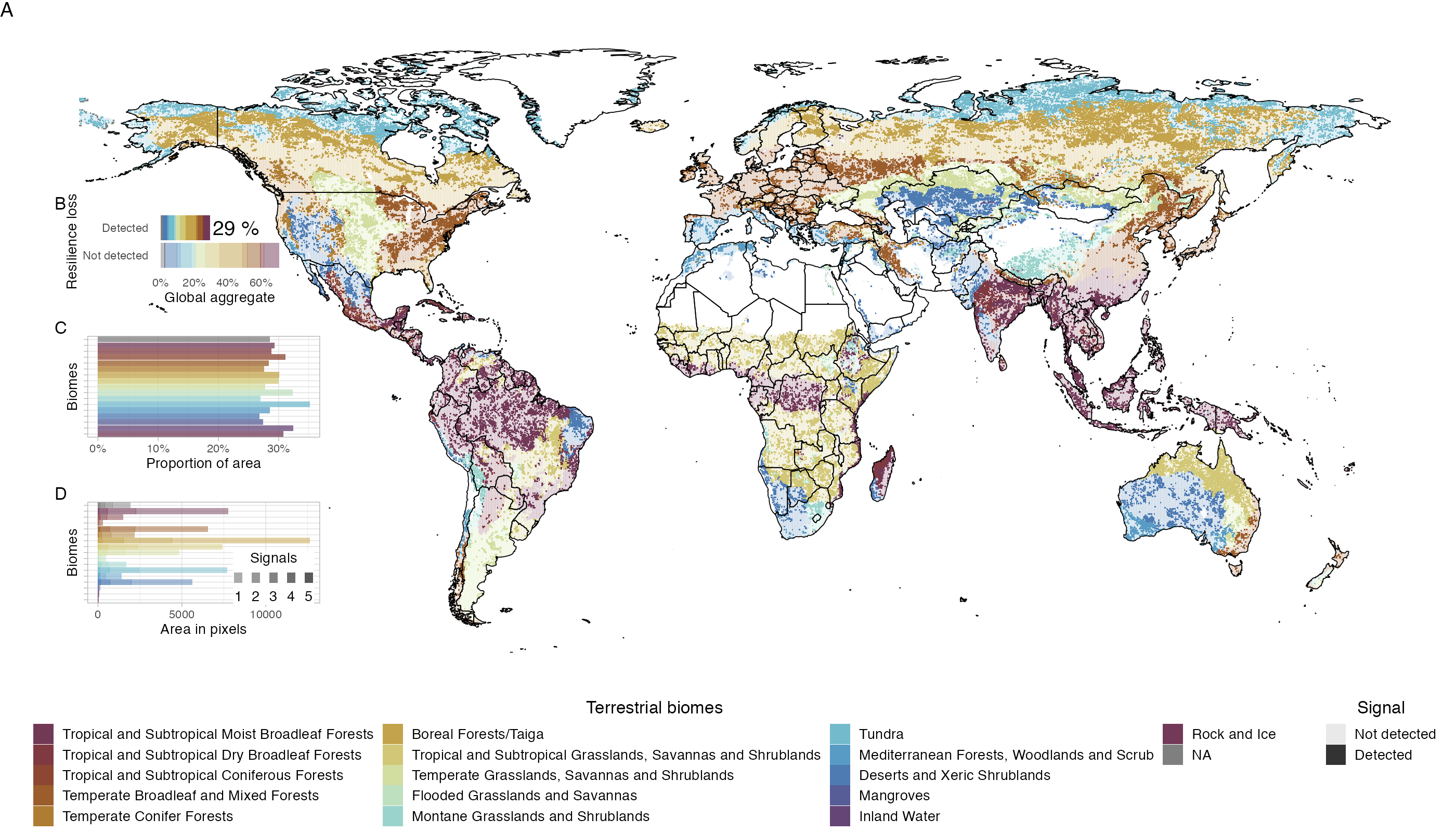
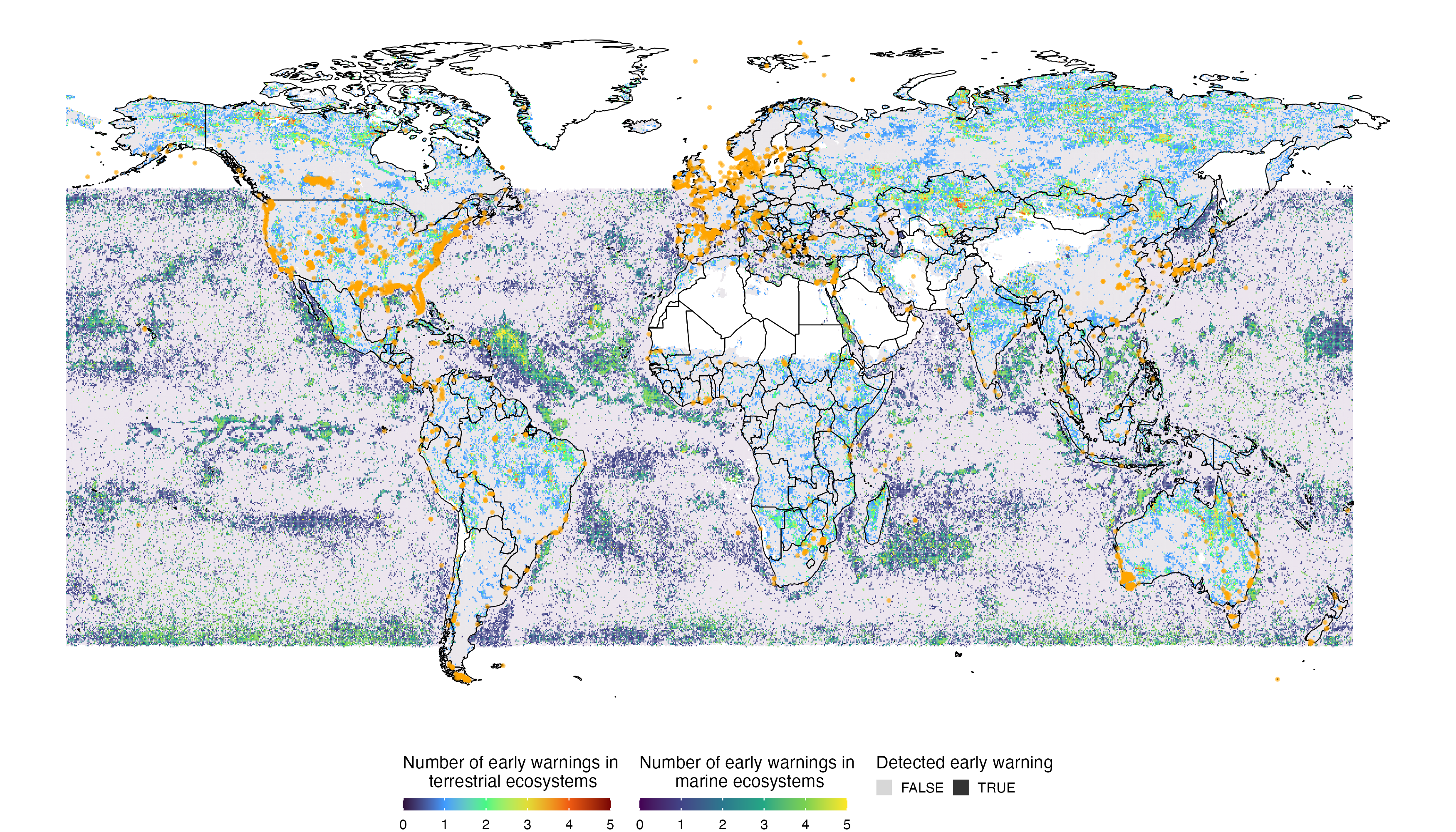
~30% of ecosystem show symptoms of resilience loss, boreal forest and tundra particularly strong signals
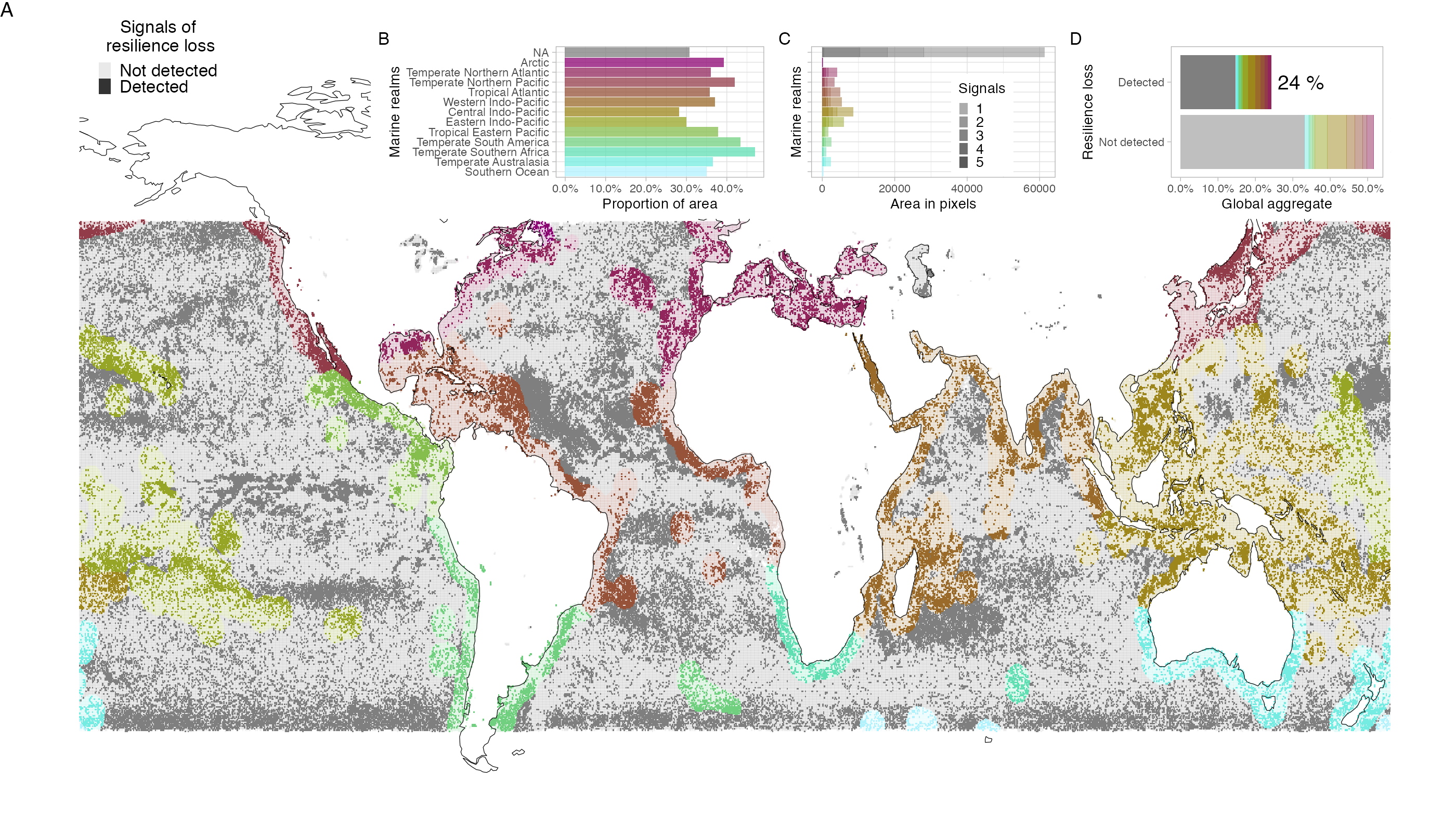
~25% of ecosystem show symptoms of resilience loss, Easter Indo-Pacific and Tropical Eastern Pacific Oceans particularly strong signals
So what?
Tipping points have impacts on people, who is exposed and who can do something about it?
Identify places prone to regime shifts
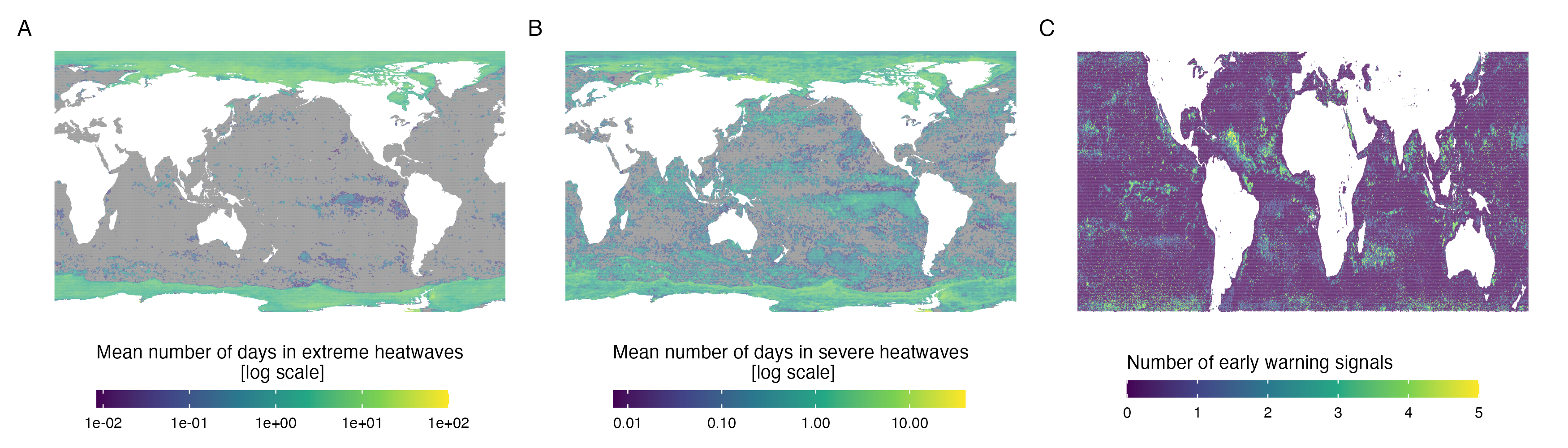
Places at risk due to drivers or showing symptoms or resilience loss
- Heatwaves: event when the SST exceeds the 99th percentile wrt 30yrs ref period1, severe and extreme events exceed 3 and 4 times the 90th percentile2
- NOAA SST observations [1981-2022 at 0.25∘] to calculate heatwave events
- ESA ocean color observations [1998-2018 at 0.25∘] to calculate proxies of resilience loss3
1Frölicher 2018 Nature ; 2Hobday 2018 Oceanography ; Smith 2023 Ann. Rev., 3Rocha 2022 ERL
Identify economic activities & companies
- >70k vessels around the world
- 16 878 vessels fishing in high risk areas
- Currently 2981 companies (Lloyds)
- For 855: 1825 shareholders (Orbis)
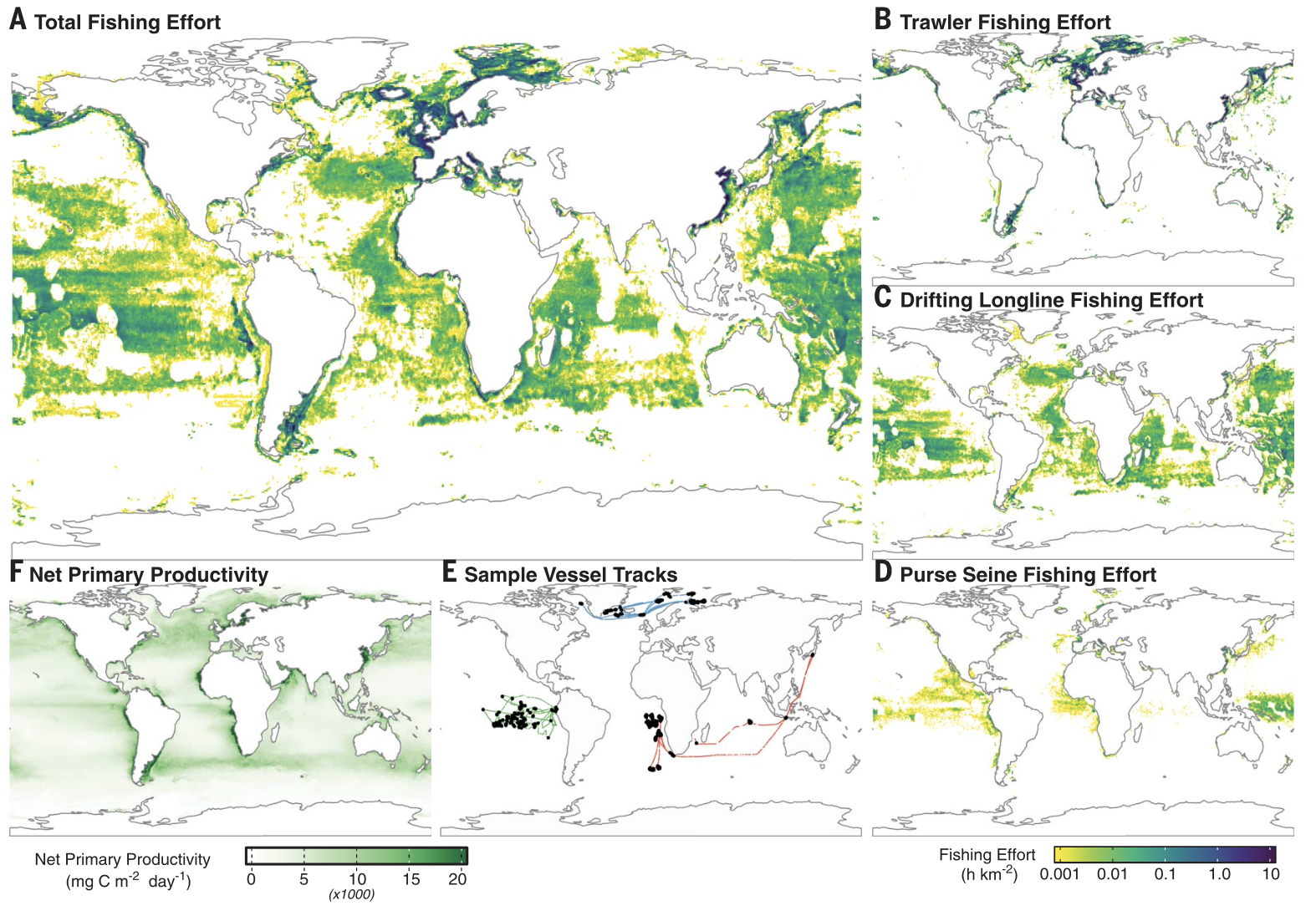
Kroodsma 2018 Science (N = 70k vessels)
Global Fish Watch V2.0 (N = 114k vessels)
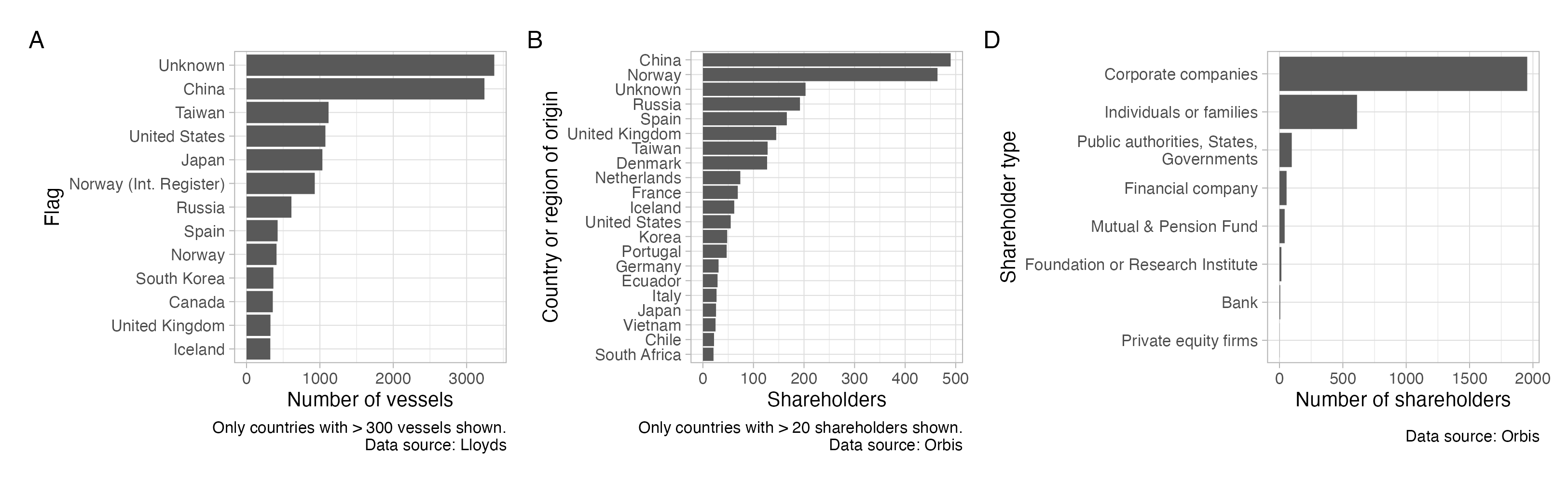
Who can make a difference?
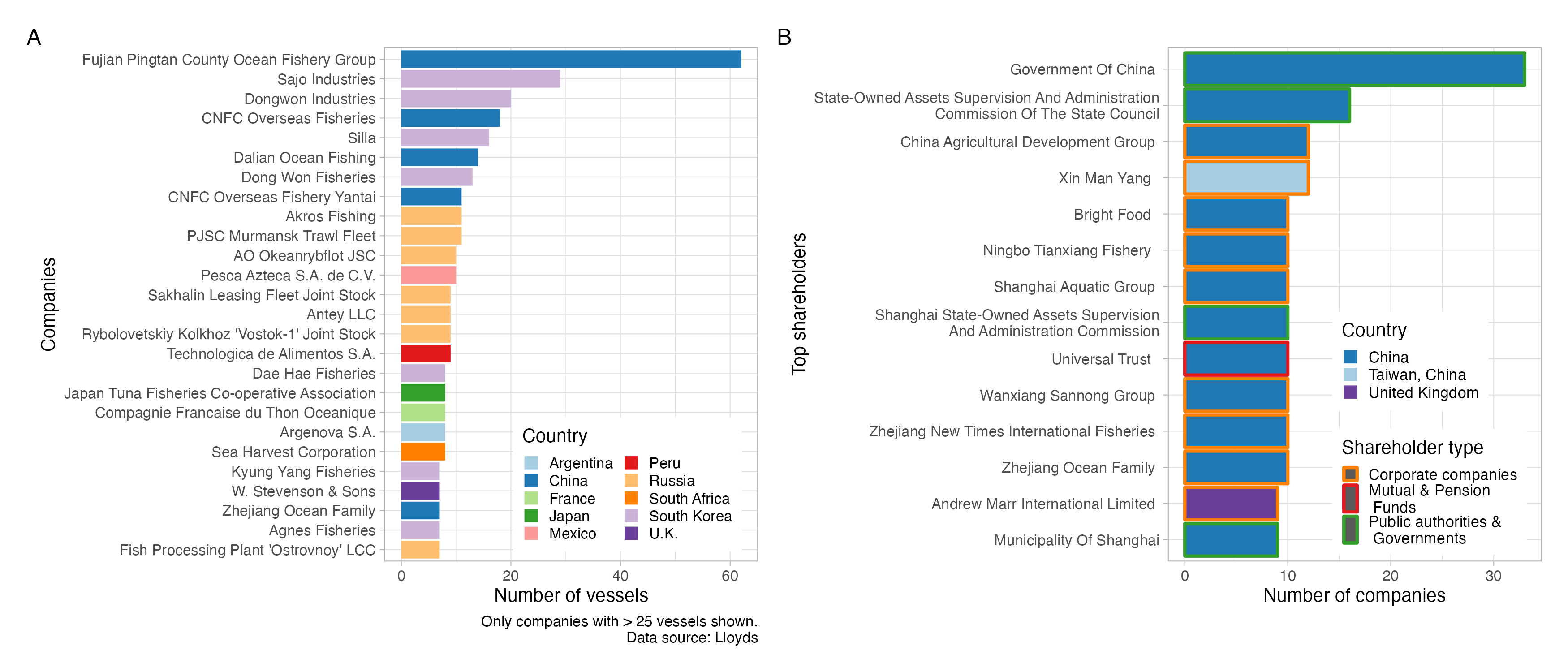
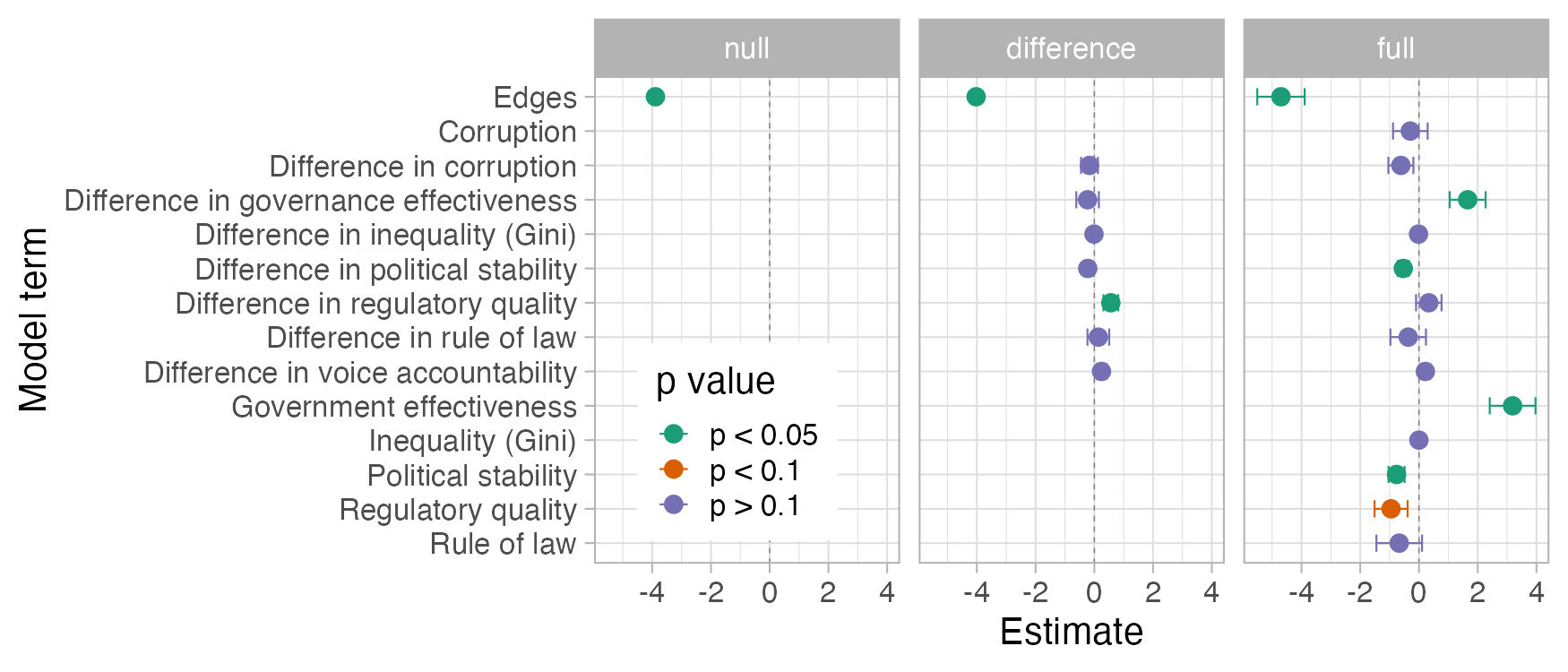
Networks: micro-macro dynamics
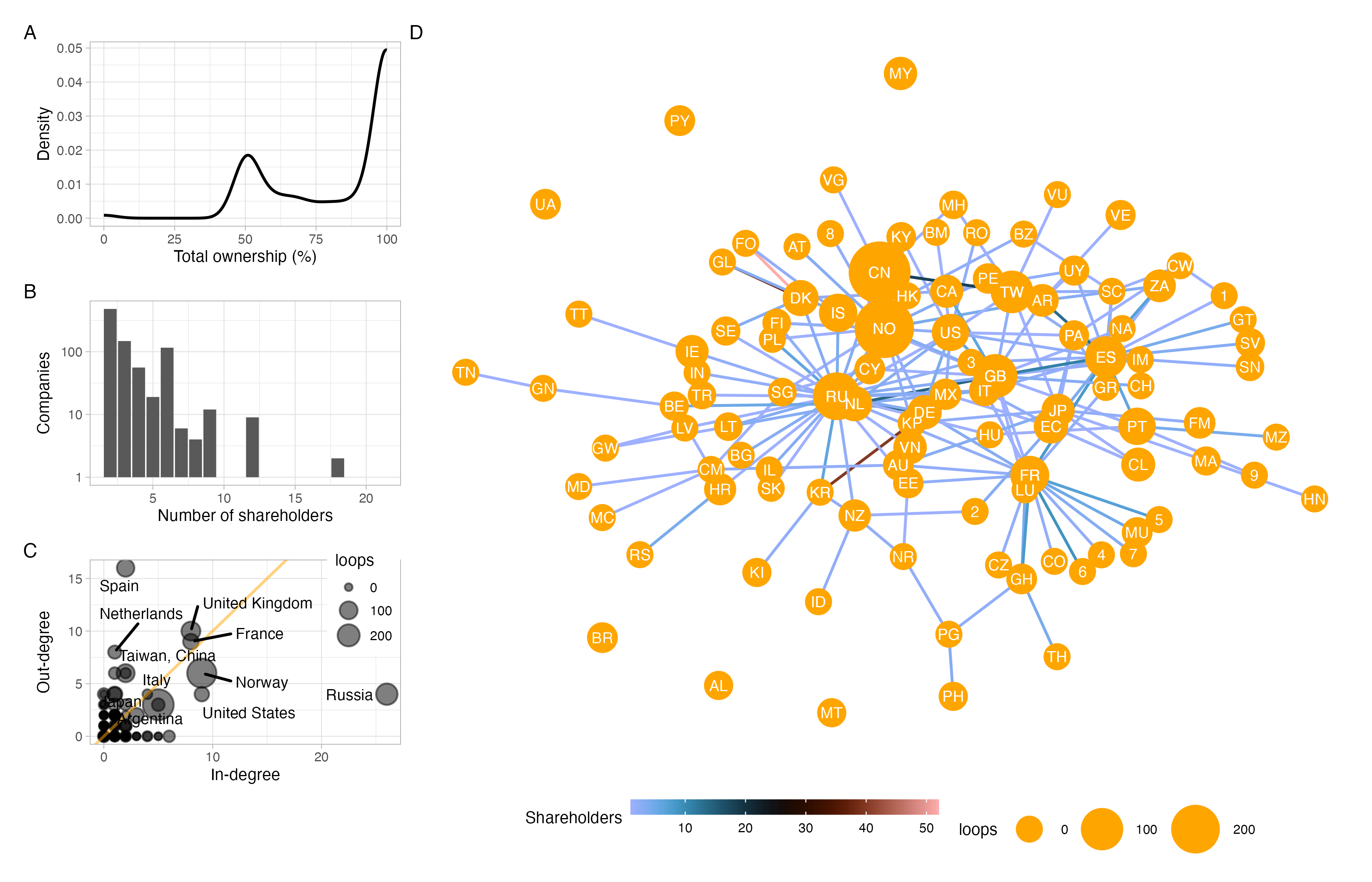
Networks: micro-macro dynamics
Conclusions
- Ecosystems around the world are showing symptoms of resilience loss
- ~30% of terrestrial and ~25% of marine areas
- Identify who is exposed and can do something about it
- Identify areas for management
Questions?: juan.rocha@su.se
Paper: Rocha, J 2022 ERL | Pre-print: https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.10307

