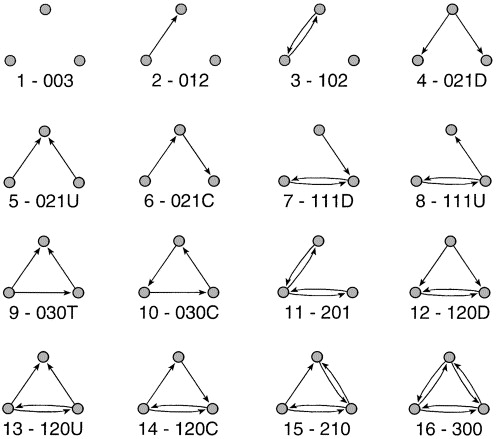
- Adjacency matrix (squared)
- Symmetric = Undirected
- Asymmetric = Directed
- Incidence matrix (rectangular)
- Bipartite / hypergraphs
- Edgelist
- Jargon check
- Node = vertex
- Link = edge = arc
- Network = graph
Networks

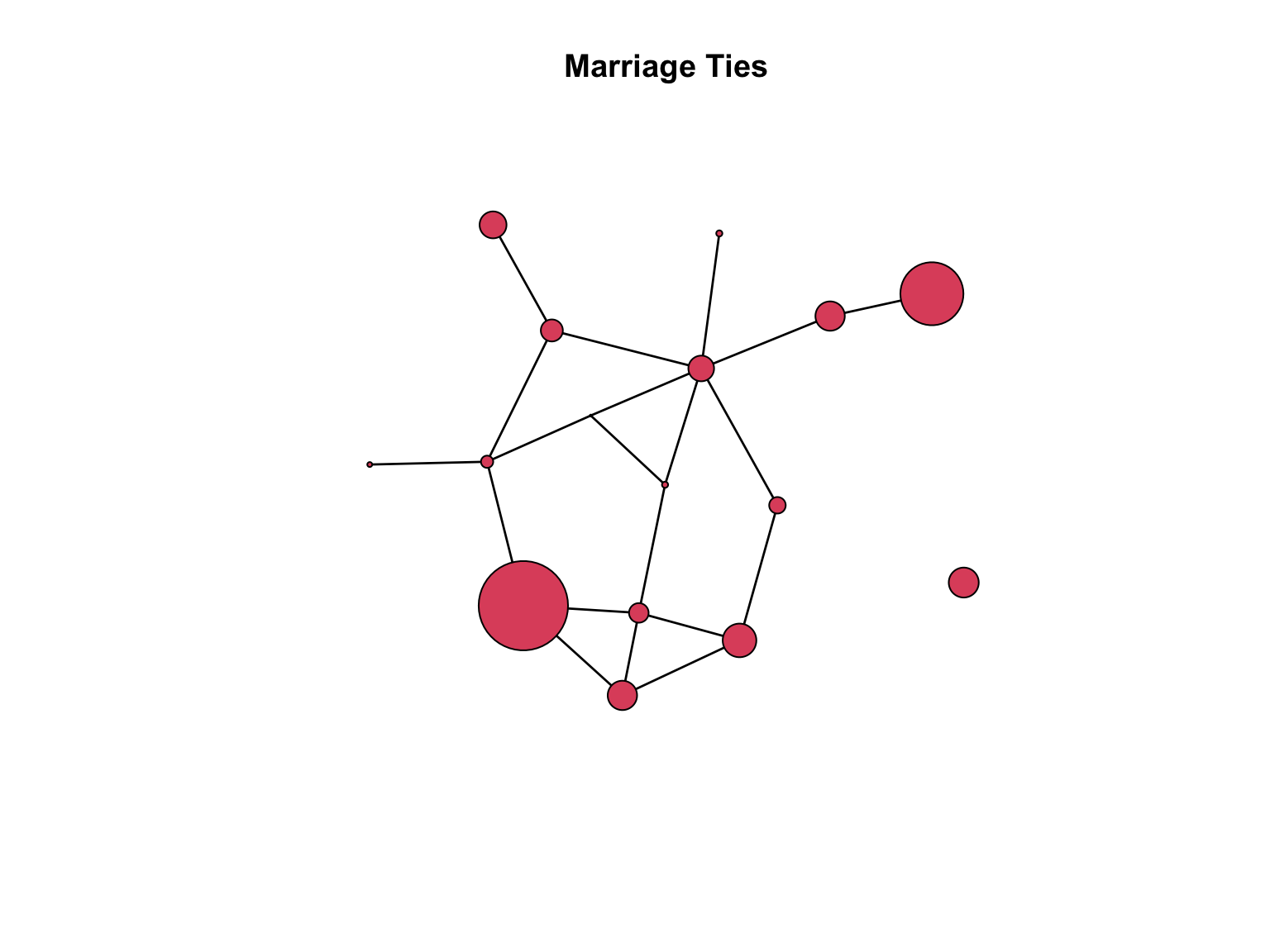
Martin Grandjean, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Quiz
What are the basic data structures in R?
Objects & Classes
| Dimensions | Homogeneous | Heterogeneous |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vector | List |
| 2 | Matrix | Data Frame |
| 3 | Array | NA |
Networks are matrices
A=[a11a12a13…a1na21a22a23…a2n⋮⋮⋮⋱⋮ad1ad2ad3…adn]
Aij= 1 if there is a link from j to i, 0 otherwise
Networks in R
statnet::network
- Social sciences and statistics
- Strong support for statistical modelling
- Network size = small - medium
igraph
- Computer science and math
- Strong support for algorithms
- Network size = large
statnet
Create a network
library(network)
mat <- matrix(rbinom(25,1,0.3), 5,5)
diag(mat) <- 0
net <- network(mat)
summary(net)## Network attributes:
## vertices = 5
## directed = TRUE
## hyper = FALSE
## loops = FALSE
## multiple = FALSE
## bipartite = FALSE
## total edges = 5
## missing edges = 0
## non-missing edges = 5
## density = 0.25
##
## Vertex attributes:
## vertex.names:
## character valued attribute
## 5 valid vertex names
##
## No edge attributes
##
## Network adjacency matrix:
## 1 2 3 4 5
## 1 0 0 0 0 0
## 2 1 0 0 0 1
## 3 0 0 0 0 1
## 4 0 0 0 0 0
## 5 0 0 1 1 0statnet
Adjacency matrix are used in bipartite graphs
library(network)
mat <- matrix(rbinom(30,1,0.3), 6,5)
diag(mat) <- 0
net <- network(mat)
summary(net)## Network attributes:
## vertices = 11
## directed = FALSE
## hyper = FALSE
## loops = FALSE
## multiple = FALSE
## bipartite = 6
## total edges = 10
## missing edges = 0
## non-missing edges = 10
## density = 0.1818182
##
## Vertex attributes:
## vertex.names:
## character valued attribute
## 11 valid vertex names
##
## No edge attributes
##
## Network adjacency matrix:
## 7 8 9 10 11
## 1 0 0 0 0 0
## 2 1 0 0 1 1
## 3 1 0 0 0 0
## 4 1 1 0 0 0
## 5 1 0 1 0 0
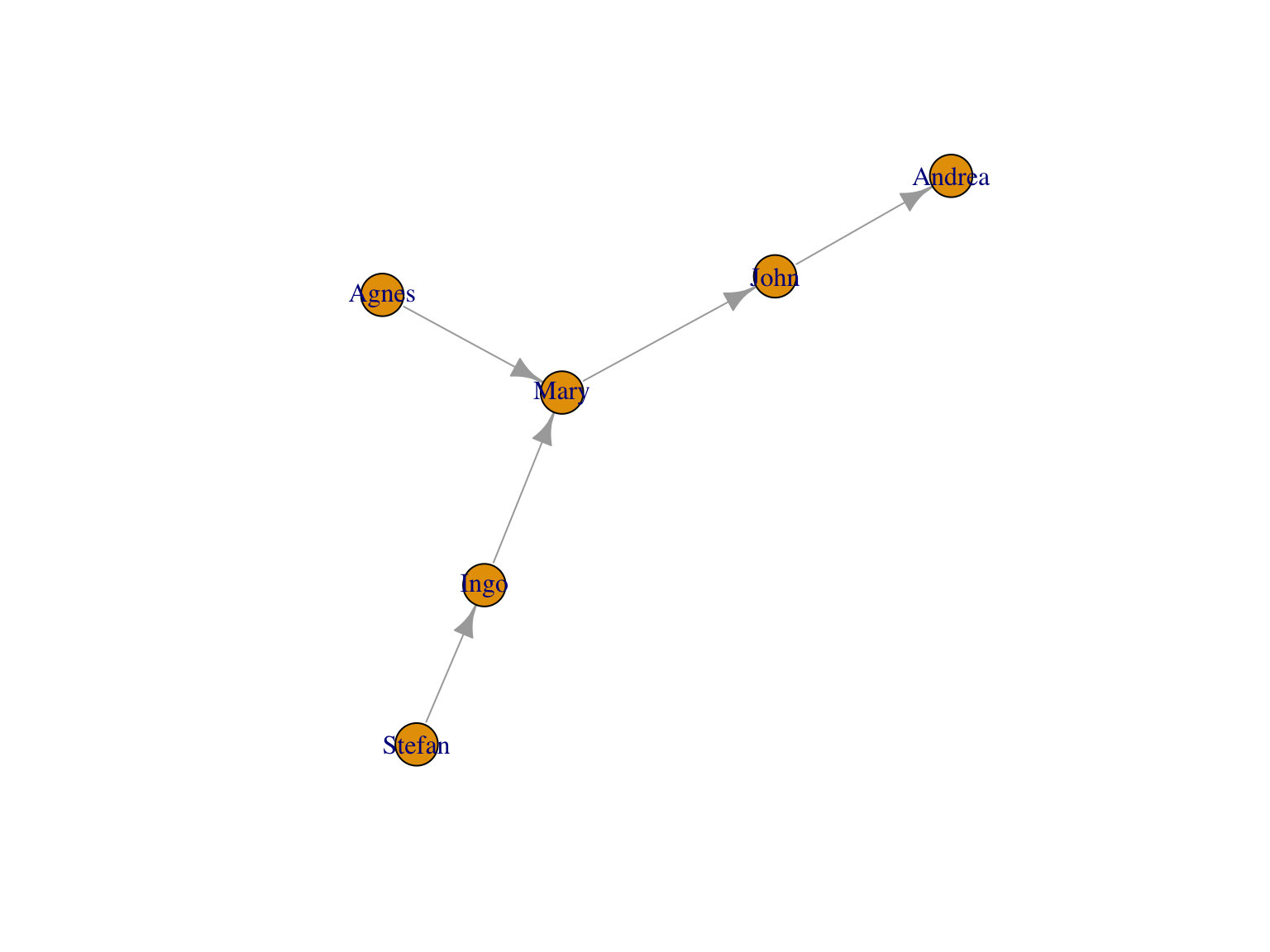
## 6 1 0 1 0 0Edgelists allow for more compact formats
library(tidyverse)
dat <- tribble(
~from, ~to, ~value,
"Agnes", "Mary", 4,
"John", "Andrea", 2,
"Mary", "John", 1,
"Ingo", "Mary", 6,
"Stefan", "Ingo", 1
)
net <- network(dat)
summary(net)## Network attributes:
## vertices = 6
## directed = TRUE
## hyper = FALSE
## loops = FALSE
## multiple = FALSE
## bipartite = FALSE
## total edges = 5
## missing edges = 0
## non-missing edges = 5
## density = 0.1666667
##
## Vertex attributes:
## vertex.names:
## character valued attribute
## 6 valid vertex names
##
## Edge attributes:
##
## value:
## numeric valued attribute
## attribute summary:
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 1.0 1.0 2.0 2.8 4.0 6.0
##
## Network adjacency matrix:
## Agnes John Mary Ingo Stefan Andrea
## Agnes 0 0 1 0 0 0
## John 0 0 0 0 0 1
## Mary 0 1 0 0 0 0
## Ingo 0 0 1 0 0 0
## Stefan 0 0 0 1 0 0
## Andrea 0 0 0 0 0 0Network statistics
Who is more central?
sna: social network analysis
library(sna)
net <- network(
rgraph(n = 30, tprob = 0.15, mode = "graph")) #digraph for directed
# number of connections
degree(net)## [1] 4 10 10 8 6 2 4 4 6 6 10 12 2 14 8 6 8 8 6 6 12 18 12 10 10
## [26] 12 10 6 10 4On a directed network you will have in- and out- degree.
Butts, T. 2008. Social Network Analysis with sna. Journal of Statistical Software
Network statistics
Betweenness measures the extent to which a vertex lie in the paths between other vertices
plot.network(
net, edge.col = "grey75", edge.lwd = 0.05,
vertex.cex = betweenness(net, gmode = "graph")/10)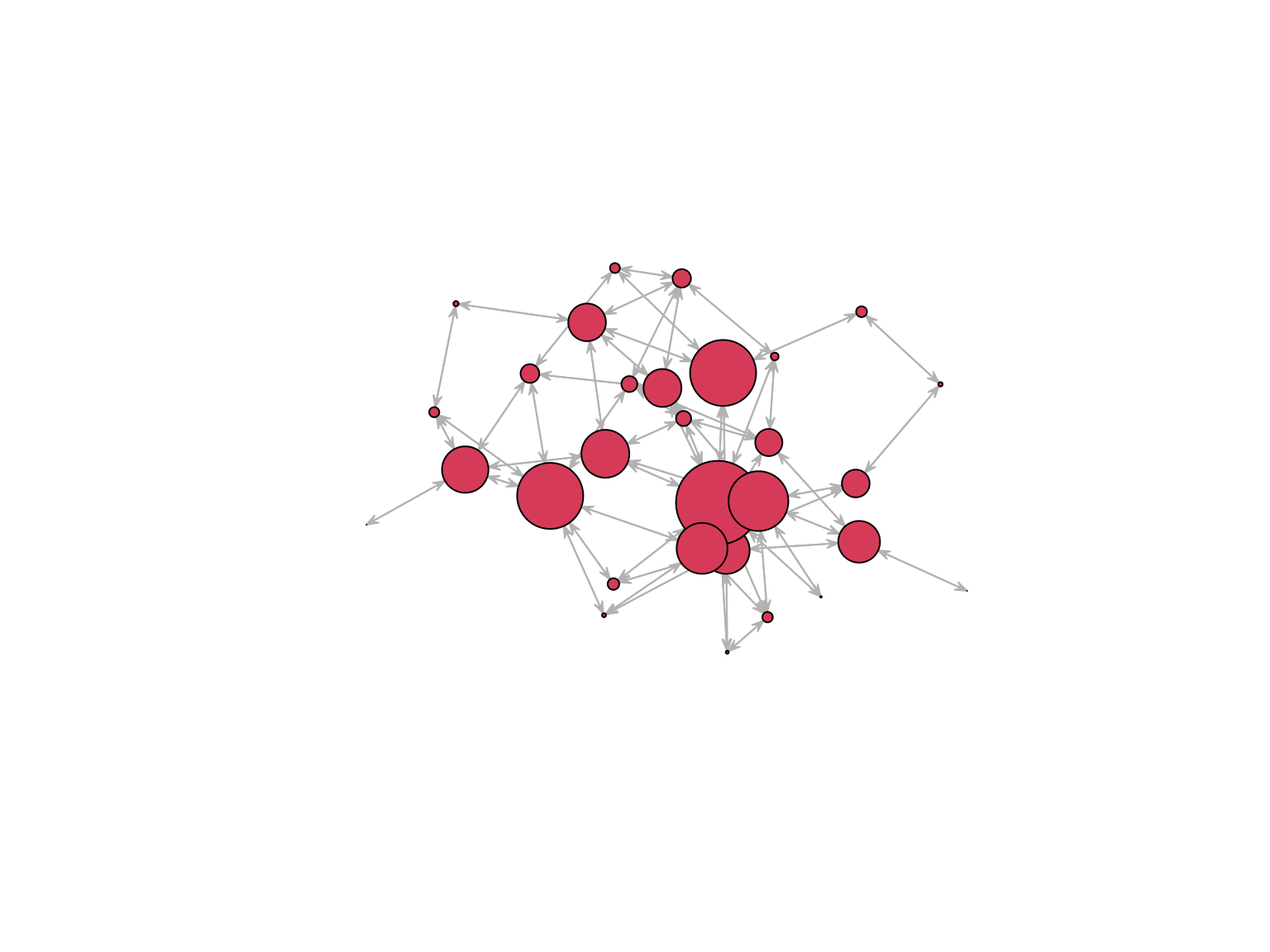 On a directed network direction is accounted for.
On a directed network direction is accounted for.
Closeness is the mean distance from a vertex to other vertices
Butts, T. 2008. Social Network Analysis with sna. Journal of Statistical Software
Centrality
- Degree
- Betweenness
- Closeness
- Eigenvector
- PageRank
- Katz
- Hubs
- Bonacich Power
- Cliques and cores
Example
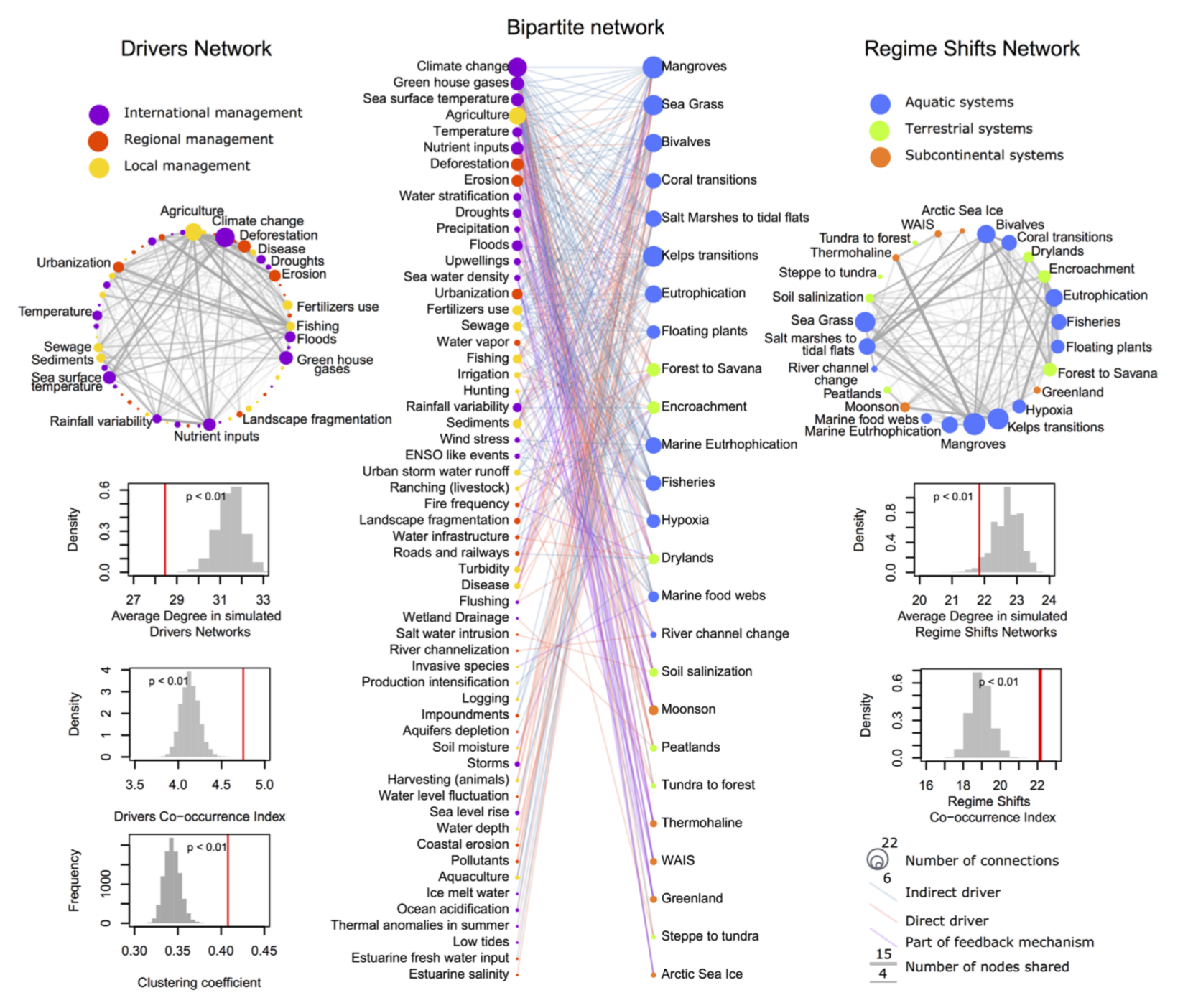
One mode vs bipartite
Most network operations are simply linear algebra on matrices
A1=BBT A2=BTB
Useful math to study co-authorship networks, people and groups (e.g. company boards, investors), affiliation, co-occurrence, pollination, gene-disease, drug discovery, among many others
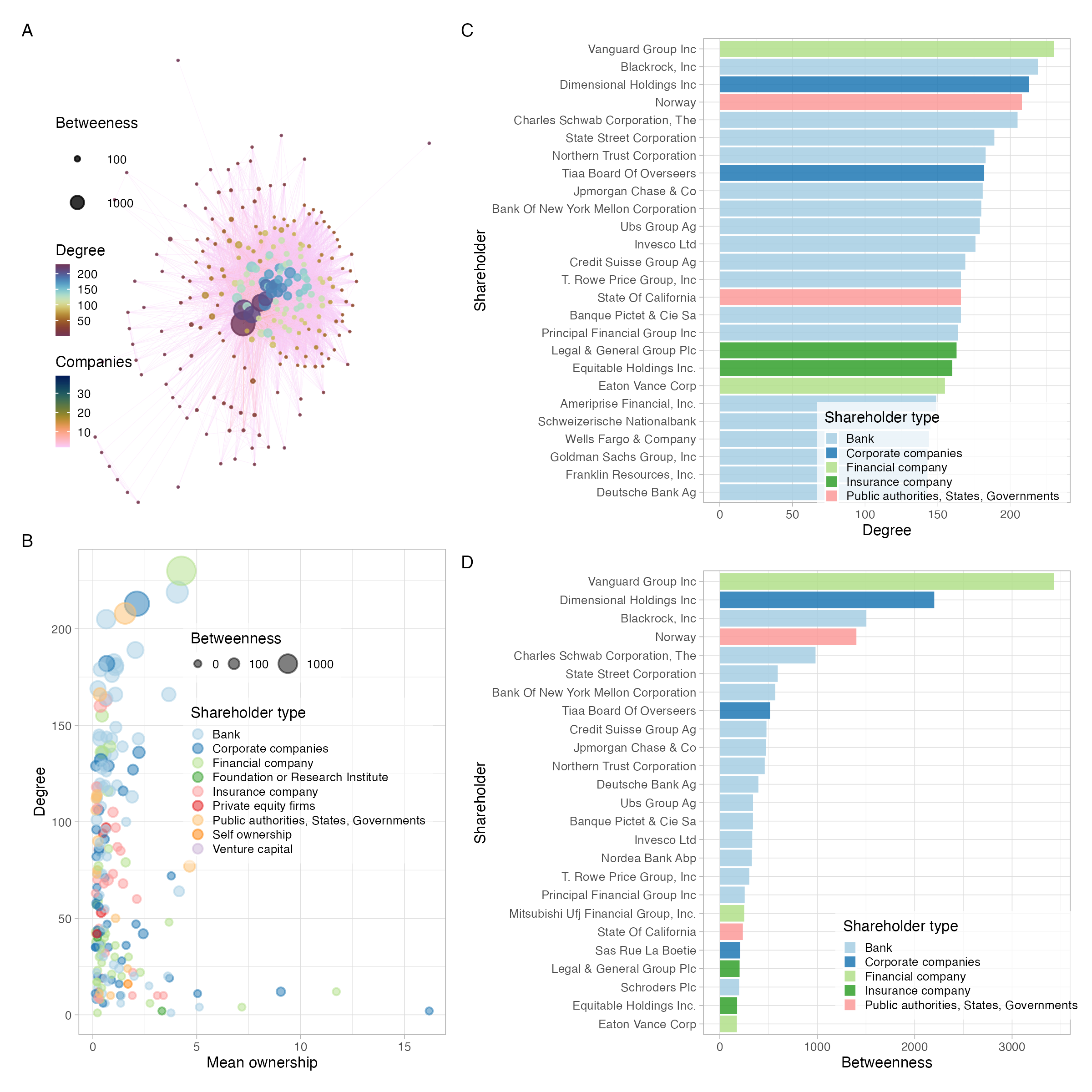
Who has the agency to make a difference?
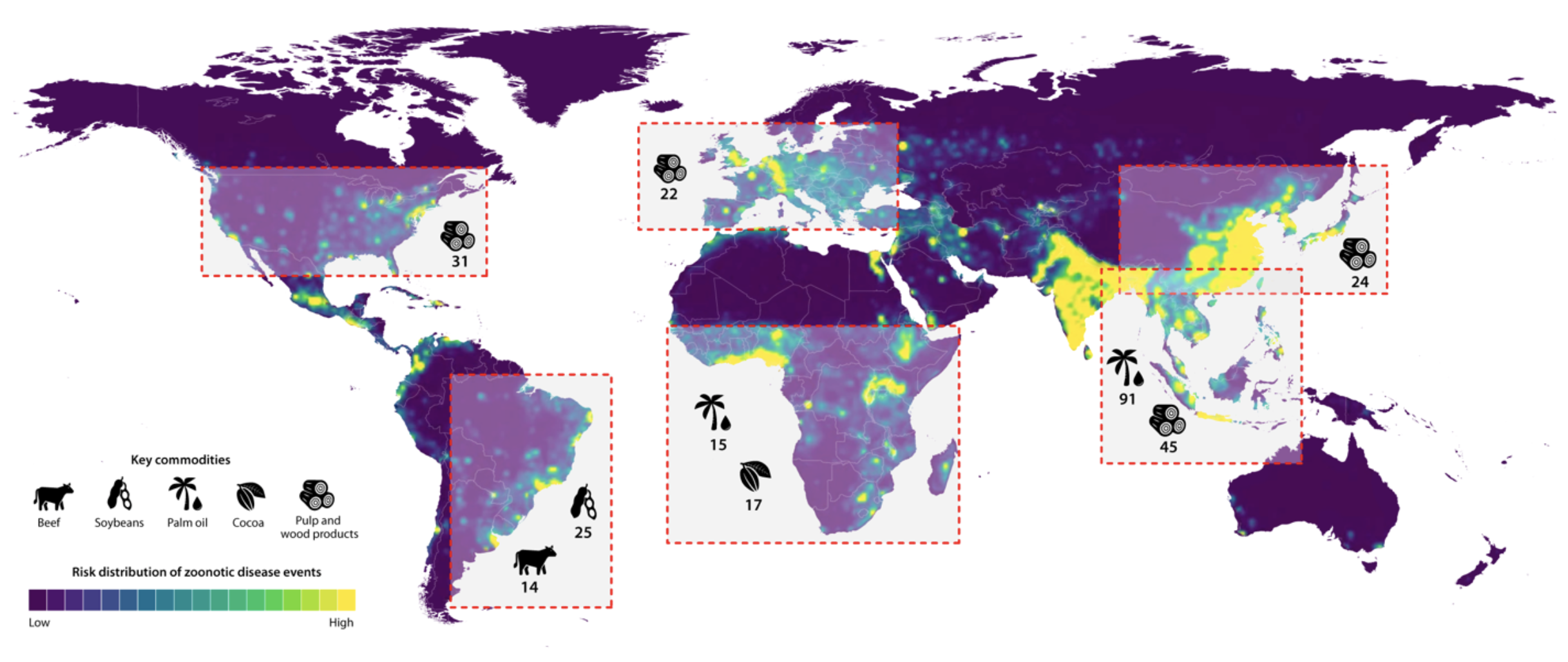
- “Zoonotic EID risk is elevated in
forested tropical regions experiencing land-use changes and where
wildlife biodiversity is high” Allen et al
2017
- Companies who extract natural resources
- Shareholders who invested in them
- Networks of shareholders with common investments
Another example: path analysis
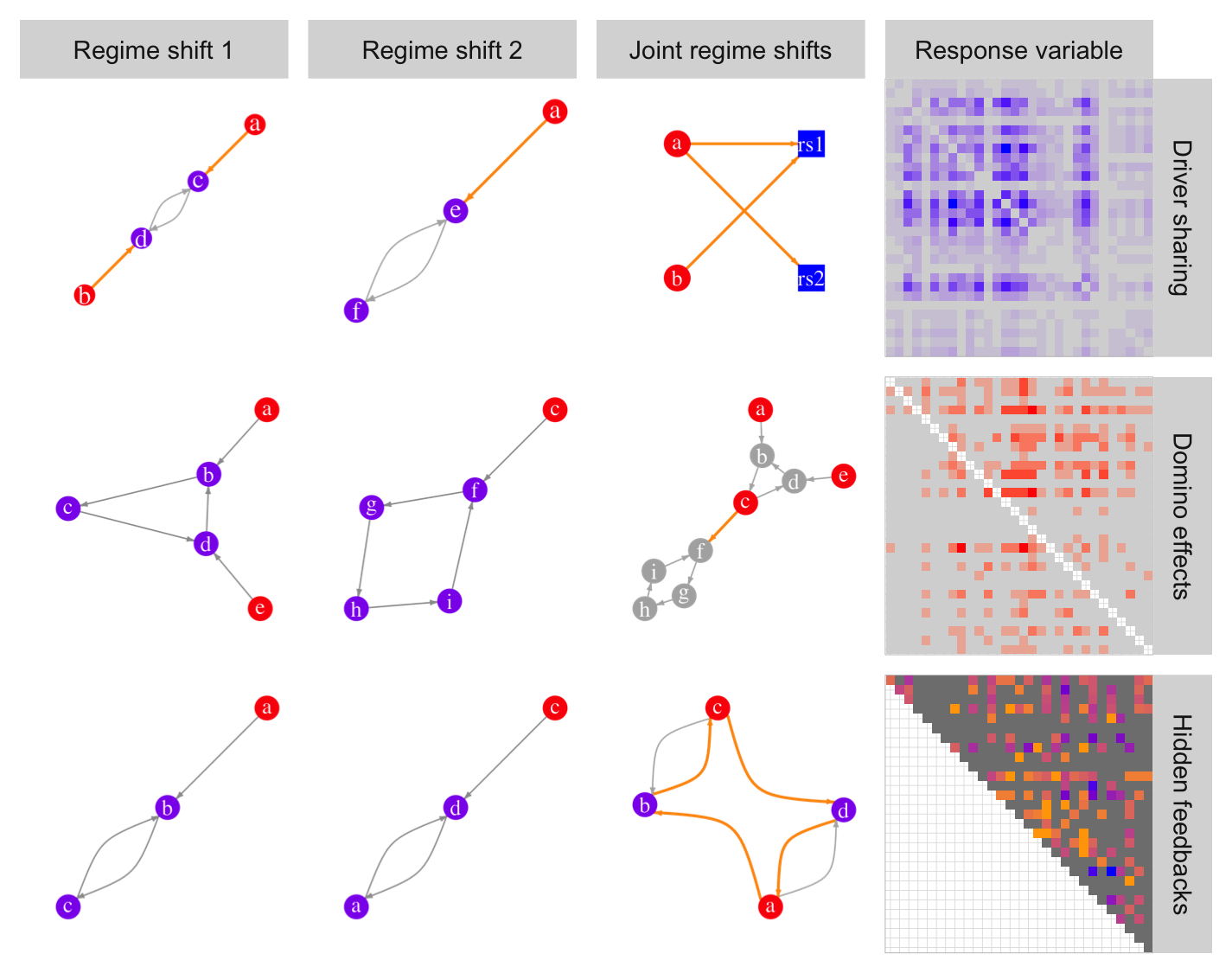
Rocha, J, et al . Cascading regime shifts within and across scales. Science 362, 1379–1383 (2018)
A worked example

Cascading effects
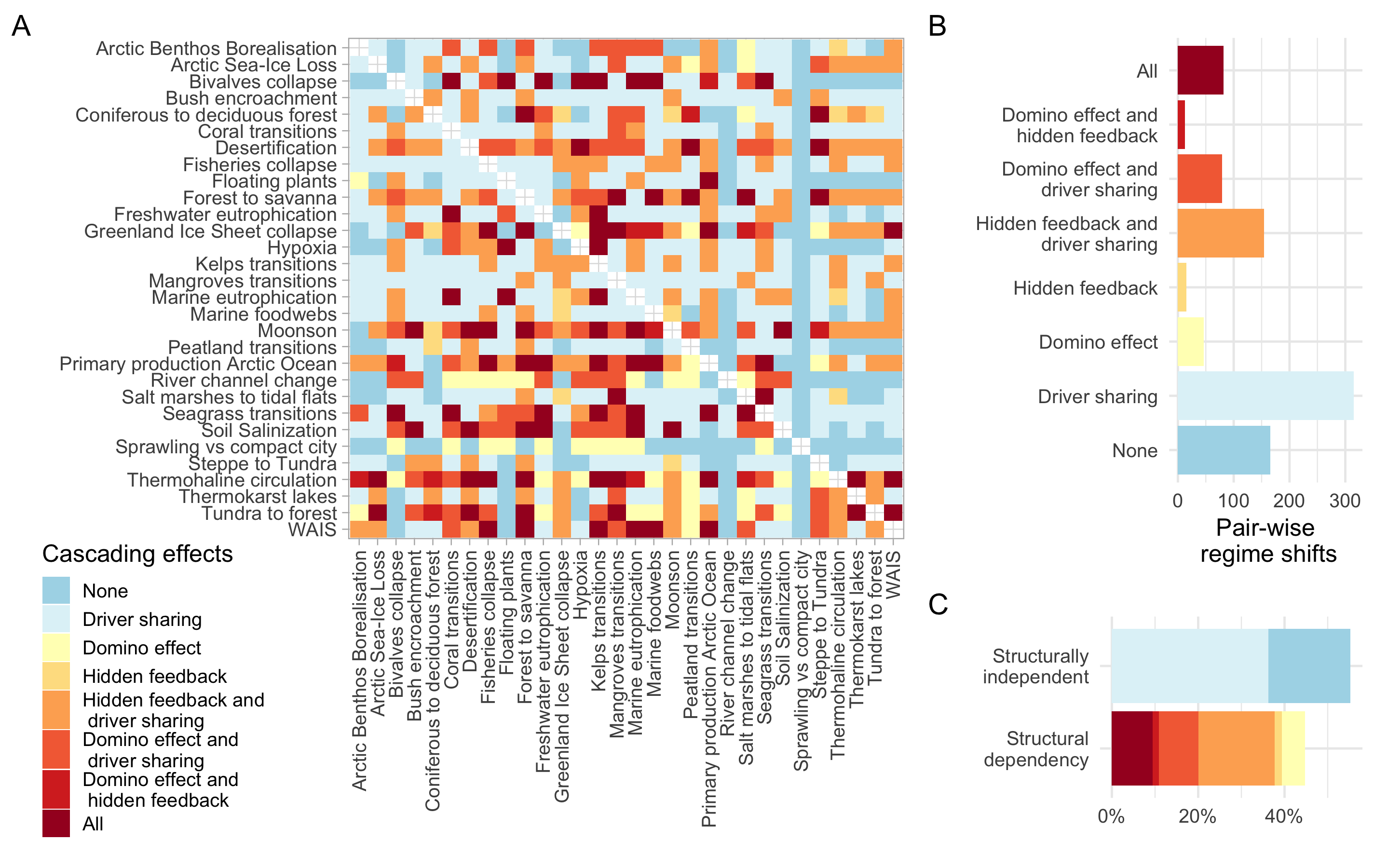
~45% of the regime shift couplings analyzed present structural dependencies in the form of one-way interactions for the domino effect or two-way interactions for hidden feedbacks
igraph
- Strong focus on algorithms
- Optimized to handle large objects
- Slightly different syntax
Be aware of conflicts between packages
##
## Attaching package: 'igraph'## The following objects are masked from 'package:lubridate':
##
## %--%, union## The following objects are masked from 'package:dplyr':
##
## as_data_frame, groups, union## The following objects are masked from 'package:purrr':
##
## compose, simplify## The following object is masked from 'package:tidyr':
##
## crossing## The following object is masked from 'package:tibble':
##
## as_data_frame## The following objects are masked from 'package:stats':
##
## decompose, spectrum## The following object is masked from 'package:base':
##
## unionigraph
Create a graph
## IGRAPH 578bfae DN-- 6 5 --
## + attr: name (v/c)
## + edges from 578bfae (vertex names):
## [1] Agnes ->Mary John ->Andrea Mary ->John Ingo ->Mary Stefan->IngoOther options
Complex objects
Networks are complex objects:
- Matrix or edgelist
- Node attributes
- Edge attributes
Useful for visualization and statistical modelling
Vertex attributes
statnet
Edge attributes
statnet
igraph
## + 5/5 edges from 578bfae (vertex names):
## [1] Agnes ->Mary John ->Andrea Mary ->John Ingo ->Mary Stefan->Ingo## $sport
## [1] "chess" "swimming" "swimming" "climbing" "fencing"## [1] "chess" "swimming" "swimming" "climbing" "fencing"Network modelling
Mechanisms for network formation
- Random (Erdos-Renyi)
- Small-world (Watts-Strogatz)
- Preferential attachment (Barabasi-Albert)
- Homophily vs influence
- Assortativity
- Motifs mixture
You want to test if your observed network has features that are signature of an underlying process or theory (e.g. assortativity ~ triangles), and compare how your hypothesis differs from a random reference point.
Network modelling
detach(package:igraph)
library(ergm)
data(flo)
flomarriage <- network(flo,directed=FALSE)
flomarriage %v% "wealth" <- c(10,36,27,146,55,44,20,8,42,103,48,49,10,48,32,3)
fit1 <- ergm(flomarriage ~ edges + absdiff("wealth"))
summary(fit1)## Call:
## ergm(formula = flomarriage ~ edges + absdiff("wealth"))
##
## Maximum Likelihood Results:
##
## Estimate Std. Error MCMC % z value Pr(>|z|)
## edges -1.457666 0.354532 0 -4.112 <1e-04 ***
## absdiff.wealth -0.004176 0.007387 0 -0.565 0.572
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Null Deviance: 166.4 on 120 degrees of freedom
## Residual Deviance: 107.8 on 118 degrees of freedom
##
## AIC: 111.8 BIC: 117.4 (Smaller is better. MC Std. Err. = 0)ergm: exponential random graph modelsergm.multi: for multilayer networkstergm: time varying networks (withtsna)ergm.count: weighted networksergm.rank: rank value modellingbergm: Bayessian ERGM (btergmfor time)EpiModelhergm: hierarchical
Network modelling
## Call:
## ergm(formula = flomarriage ~ edges + absdiff("wealth") + triangle)
##
## Monte Carlo Maximum Likelihood Results:
##
## Estimate Std. Error MCMC % z value Pr(>|z|)
## edges -1.467774 0.503880 0 -2.913 0.00358 **
## absdiff.wealth -0.004324 0.007631 0 -0.567 0.57095
## triangle 0.072487 0.602304 0 0.120 0.90421
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Null Deviance: 166.4 on 120 degrees of freedom
## Residual Deviance: 107.8 on 117 degrees of freedom
##
## AIC: 113.8 BIC: 122.1 (Smaller is better. MC Std. Err. = 0.00496)Visualization
plot()commands from each packagenetworkD3wraps a nice java script library (interactive)ggnetwork&ggraphusesggplotsyntaxgraphpackage (circular plots)circlospackage for chord diagrams (interactive)
Play around with your own!
Resources
- Online tutorials (often offered in Sunbelt, NetSci)
- Katya Ognyanova: https://kateto.net/tutorials/
- Books:
- Introduction to Networks by Mark Newman (2010)
Exercise
Data
Study the academic production of SRC!
Download the Scopus record of all SRC publications by 2022
Link: https://stockholmuniversity.box.com/s/35ydfdtm8gheh1s1jsrfscj6tj9ixhog
Note: ~25MB csv file
Data
## Rows: 1870 Columns: 20
## ── Column specification ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
## Delimiter: ","
## chr (17): Authors, Author(s) ID, Title, Source title, Volume, Issue, Art. No...
## dbl (3): Year, Page count, Cited by
##
## ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data.
## ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.## # A tibble: 1,870 × 20
## Authors `Author(s) ID` Title Year `Source title` Volume Issue `Art. No.`
## <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
## 1 Röös E., W… 35746751300;4… Diag… 2023 Ecological Ec… 203 <NA> 107623
## 2 Matthews N… 55539168500;5… Elev… 2022 Water Security 17 <NA> 100126
## 3 Burgos-Aya… 57216944411;5… Less… 2022 Journal for N… 70 <NA> 126281
## 4 Bodin Ö., … 13103663000;8… A di… 2022 Progress in D… 16 <NA> 100251
## 5 West S., S… 56528901700;5… Nego… 2022 Humanities an… 9 1 294
## 6 Macura B.,… 53871480000;5… What… 2022 Environmental… 11 1 17
## 7 Selig E.R.… 16507642200;5… Reve… 2022 Nature Commun… 13 1 1612
## 8 Österblom … 6505898338;57… Scie… 2022 Scientific Re… 12 1 3802
## 9 Anderies J… 6603314876;71… A fr… 2022 Biological Co… 275 <NA> 109769
## 10 Bodin Ö., … 13103663000;3… Choo… 2022 Public Admini… 82 6 <NA>
## # ℹ 1,860 more rows
## # ℹ 12 more variables: `Page start` <chr>, `Page end` <chr>,
## # `Page count` <dbl>, `Cited by` <dbl>, DOI <chr>, Link <chr>,
## # References <chr>, `Document Type` <chr>, `Publication Stage` <chr>,
## # `Open Access` <chr>, Source <chr>, EID <chr>Exercise
Objective: Create a co-authorship network
- Parse author names, split authors field separating by commas (tips:
str_split()andunnest()). - Once you have individual authors and papers, you can construct a
bipartite network.
- As edgelist (easy)
- As matrix (less easy)
- Calculate the one-mode author-author network.
- Find a suitable threshold for visualization (do you need all people?)
- Calculate some stats of interest: e.g. who are the most central authors
- Explore
library(intergraph)to change formats fromnetworktoigraphif necessary igraphhas a variety of algorithms to detect communities. Try one and discuss the result with a colleague: Does it reflect key topics or themes at SRC?